
Beth
Multilingual, LLM-based Conversational Platform

Large Language Models (LLM) as Platform for Virtual Assistants
Our LLM-based platform Beth has been designed to facilitate the creation and implementation of next-generation intelligent virtual assistants to serve corporations and their stakeholders in various industries (including heavily regulated ones such as Banking, Insurance and Telecoms).
Based on the revolutionary ChatGPT Large Language Model, Beth transforms the way clients and employees interact with the company, access its services and execute operations. Built on unique, proprietary architecture, Beth effectively utilizes a set of deep-learning LLMs developed by OpenAI to bring unparalleled coprehension of human language pushing their application boundaries further. These models have numerous advantages over traditional NLP models, such as understanding long and complex sentences, capability to generate natural, structured and coherent text and understanding instructions in the form of prompts.
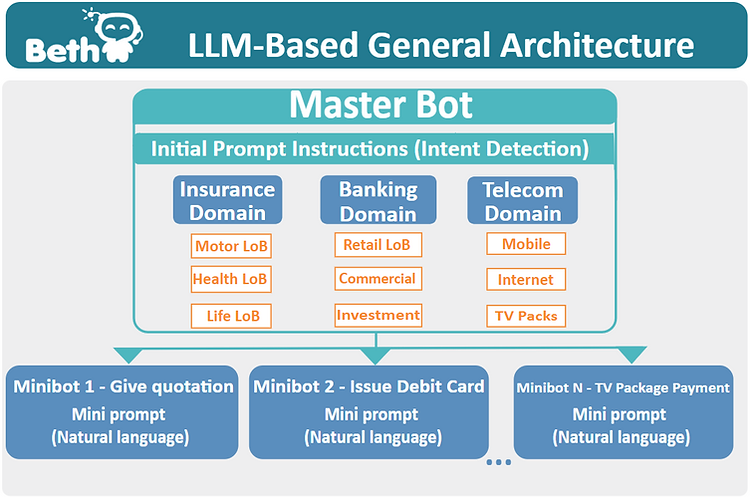
The enormous potential and the advantages of LLMs over tradition NLP, make their application in customer service immensely appealing. However, the nature of deep neural networks used, raise concerns over the degree of control and predictability of the so called 'black box' output. These concerns can be summarized as:
-
Vulnerability to bias: LLMs can produce discriminatory outputs due to biased data, leading to potential losses in revenue or customer dissatisfaction.
-
Lack of transparency: LLMs operate as a "black box," making it difficult to determine why a specific output was generated, raising concerns in high-stakes decision-making scenarios.
-
Hallucination: Over-trained LLMs may generate nonsensical or inaccurate information, leading to misinformed decisions, compliance risks, difficulty in customization, inefficient use of resources, and potential harm to brand reputation.
-
Limited programming interface: The current API only allows communication via natural language, making it challenging to collect data or impose constraints on text completion.
These challenges must be addressed to fully harness the potential of LLMs in a corporate context and regulated fields, such as financial services, telecoms and even health care.
How we solved these challenges in Beth
Ablera's LLM-based platform for Intelligent Virtual Assistants (IVA) addresses the challenges posed by taming LLMs and effectively bring them under control. The platform, designed for corporate business, focuses on three main strategies:
-
Intercepting LLM thoughts by using specifically designed prompts and labeling user intent,
-
Eliminating hallucinations by using GPT labels to detect user intent and overwrite GPT messages with predefined messages
-
Token optimization, which involves separating logically isolated tasks to reduce tokens and improve efficiency. These approaches help avoid hallucinations, stabilize conversations, and maintain the conversational skills of the Assistant.
Taming LLMs with Prompt Engineering

Beth's capabilities stem from the "prompt engineering" we use for intent recognition, a crucial feature of the robust and reliable virtual assistant. Traditional NLP models struggle with intent recognition, leading to high churn (abandon) rates and user dissatisfaction. Ablera's LLM-based approach offers several advantages over traditional methods:
-
It uses instruct-LLM models to analyze conversations and recognize user intent similarly to a human assistant.
-
It defines intents as instructions through detailed natural language descriptions rather than relying on a large database of utterances.
-
The virtual assistant can maintain conversations, allowing multiple attempts to recognize user intent while gathering more relevant information.
-
A multi-layer architecture of intent recognition can classify intents into groups, reducing the number of intents per prompt and allowing the approach to scale.
Ablera's approach enables LLM models like GPT-n to be effectively utilized for customer service in intelligent virtual assistants, addressing limitations and concerns in highly regulated industries such as financial services.
We have developed a robust methodology that businesses can implement, consisting of a combination of approaches, such as fine-tuning techniques, integrating domain-specific knowledge bases, and utilizing rule-based systems related to corporate specific answer store to ensure more accurate and contextually relevant responses. Moreover, Ablera’s Beth is already in an implementation phase not only in Banking, but also in the Insurance domain, and the already built methodology is backed-up with real-life examples.
Ablera’s goal is to illustrate how a heavily regulated institutions can build their virtual agents and “super employees”, step-by-step , eliminating the risks associated with LLMs while utilizing their strengths. The methodology is a subject of continuous review and extended day by day, driven by the accumulated knowledge and experience from the running projects.

Contact Us
Get in touch with us today.
We are here to help you enter the digital future successfully.
By submitting this form, I agree Ablera to save my personal data needed for this communication.
For more details, please check our Privacy Statement.